Standard Randomize Benchmarking¶
An approach to obtain the average gate fidelity is to perform randomized benchmarking [6]. The key idea is that if we average the error process over the uniform space of unitaries the result is a depolarizing channel that maps any pure state to the maximally mixed state. Such uniform space of unitaries is known as Haar measure. It can be shown [6] that the average induced error is proportional to the depolarization probability. However, this approach is inefficient because we sample randomly from the Haar measure. A simplification was proposed in [13] by restricting the unitaries to the Clifford group, which consists of unitary rotations mapping the group of Pauli operators in itself. Among the advantages of such group are the fact of the number of Clifford gates is finite given the Hilbert space and being a group we can easily found the inverse within the group. The generic procedure to perform a randomized benchmarking is the following:
initialize the system in ground state
for each sequence length \(m\) draw sequence of Clifford group elements
calculate inverse gate
measure sequence and inverse gate
repeat the process for multiple sequence of same length and varying the length
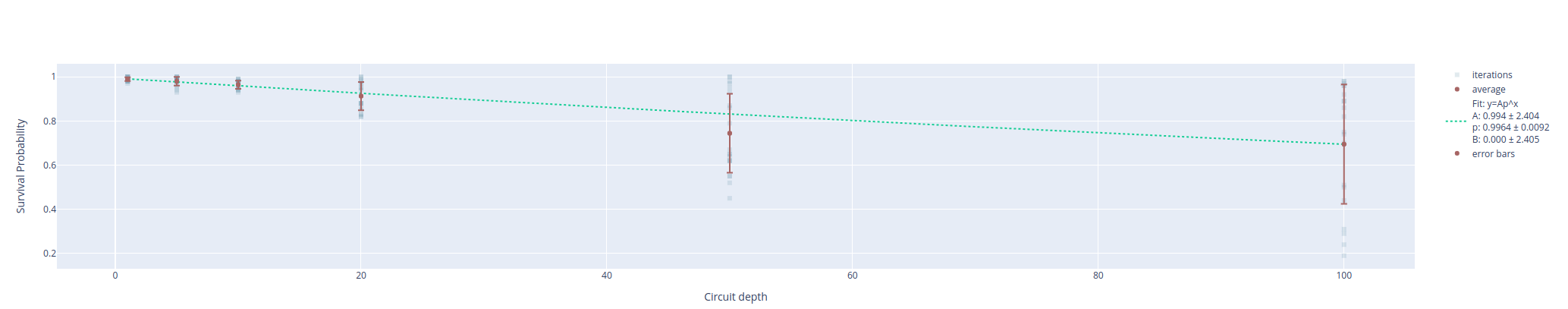
The previous approach works because it has been shown [17] that randomization with Clifford gates provides again a depolarized noise channel
with depolarization probability \(d\). If we follow the previous procedure and we measure the survival probability, i.e. the probability of measuring the qubit in \(\ket{0}\), for different sequence length \(m\) we expect the following behavior
where \(1-p\) is the rate of depolarization while \(A\) and \(B\) capture state preparation and measurement errors. Finally, we can extract the average error per Clifford as
where \(n\) is the number of qubits. The error per gate can be derived by dividing the Clifford error by the physical gates per Clifford which usually is 1.875. One of the main feature of RB is the possibility to estimate the gate fidelity alone without taking into account both state preparation and measurement errors which can be computed using the \(A\) and \(B\) terms in Eq. 2.
Parameters¶
- class qibocal.protocols.randomized_benchmarking.standard_rb.StandardRBParameters(depths: list | Depthsdict, niter: int, uncertainties: float | None = None, unrolling: bool = False, seed: int | None = None, nshots: int = 10)[source]
Standard Randomized Benchmarking runcard inputs.
- depths: list | Depthsdict
A list of depths/sequence lengths.
If a dictionary is given the list will be build.
- niter: int
Sets how many iterations over the same depth value.
- uncertainties: float | None = None
Method of computing the error bars of the signal and uncertainties of the fit.
If
None, it computes the standard deviation. Otherwise it computes the corresponding confidence interval. Defaults None.
- unrolling: bool = False
If
Trueit uses sequence unrolling to deploy multiple circuits in a single instrument call.Defaults to
False.
- seed: int | None = None
A fixed seed to initialize
np.random.Generator.If
None, uses a random seed. Defaults isNone.
- nshots: int = 10
Just to add the default value.
- hardware_average: bool = False
By default hardware average will be performed.
- relaxation_time: float
Wait time for the qubit to decohere back to the gnd state.
Example¶
It follows a runcard where we execute a standard RB.
- id: standard rb
operation: standard_rb
parameters:
depths: [1,5,10,20,50,100]
niter: 20
nshots: 100
The expected output is the following: