Time Of Flight (Readout)¶
In this section, we present the time-of-flight experiment for qibocal (see Fig.12 [9]).
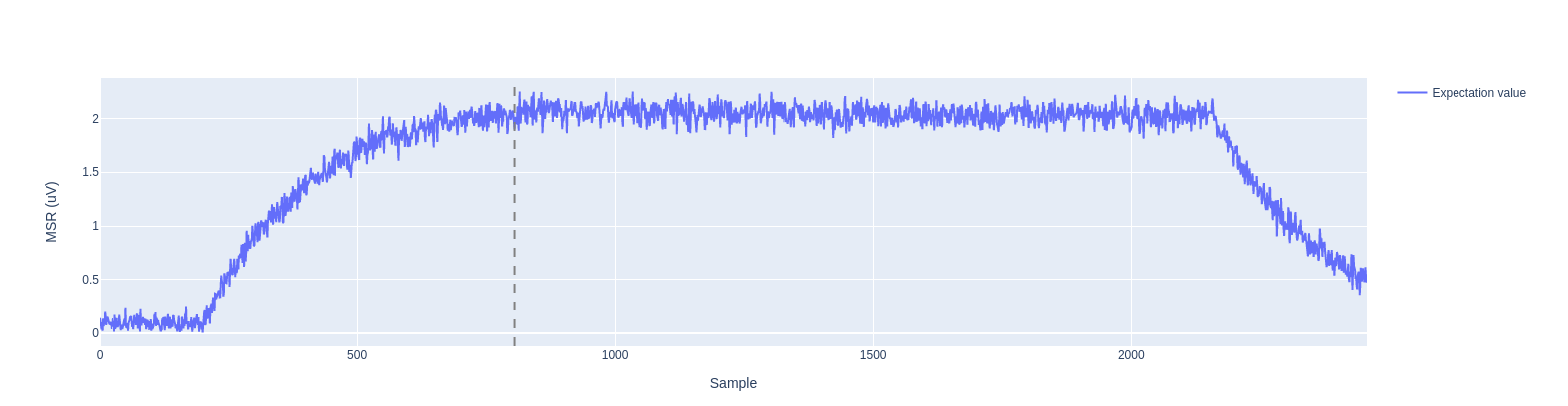
In the time of flight experiment, we measure the time it takes for a readout pulse to travel to the qubit and back, being acquired by the control instrument ADCs.
Carefully calibrating this delay time is important to optimize the readout. In particular, it is useful to acquire just for the duration of the readout pulse, where differences between the two states really appear (both in amplitude and phase).
Parameters¶
- class qibocal.protocols.signal_experiments.time_of_flight_readout.TimeOfFlightReadoutParameters(detuning: float = 10000000.0, readout_amplitude: int | None = None, window_size: int | None = 10)[source]
TimeOfFlightReadout runcard inputs.
- detuning: float = 10000000.0
Detuning with respect to corresponding LO frequency [Hz].
- hardware_average: bool = False
By default hardware average will be performed.
- nshots: int
Number of executions on hardware.
- relaxation_time: float
Wait time for the qubit to decohere back to the gnd state.
How to execute the experiment¶
- id: time of flight experiment # custom ID of the experiment
operation: time_of_flight_readout # unique name of the routine
parameters:
readout_amplitude: 0.5
window_size: 10
detuning: 50_000_000
nshots: 1024
relaxation_time: 20_000
Although it is possible to avoid setting a specific readout amplitude, it is generally useful to set a high value here. Indeed, we are not looking for the optimal amplitude but we want to have a signal with enough power so that it is clear when it starts.
Acquisition¶
Fit¶
The fit procedure computes the expected time at which the signal should appear. To estimate the time of flight in the fitting a threshold is estimated to distinguish the noise from the signal, then the first point where the signal exceed this value is selected as the time of flight.
Requirements¶
Before this experiment, nothing in particular is required. This can indeed be done as a first test of the connections.