Examples¶
Let’s now do some examples of how to use Qibosoq.
Note that, for these examples to be run, the Qibosoq server needs to be running and reachable from the client.
A standard program will be executed with something like:
import json
import socket
from qibosoq.client import execute
HOST = "192.168.0.200"
PORT = 6000
server_commands = {
"operation_code": some_object,
"cfg": some_object,
"sequence": some_object,
"qubits": [some_object],
}
i_values, q_values = execute(server_commands, HOST, PORT)
Execution of a sequence of pulses¶
To send a simple pulse sequence, we just needed to define all the server_commands to be sent with the qibosoq_execute function:
from qibosoq.client import execute
from qibosoq.components.base import (
Qubit,
OperationCode,
Config
)
from qibosoq.components.pulses import Rectangular
pulse_1 = Rectangular(
frequency = 5400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0,
duration = 0.04,
name = "drive_pulse",
type = "drive",
dac = 0,
adc = None
)
pulse_2 = Rectangular(
frequency = 6400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0.04,
duration = 2,
name = "readout_pulse",
type = "readout",
dac = 1,
adc = 0
)
sequence = [pulse_1, pulse_2]
config = Config()
qubit = Qubit()
server_commands = {
"operation_code": OperationCode.EXECUTE_PULSE_SEQUENCE,
"cfg": config,
"sequence": sequence,
"qubits": [qubit],
}
i, q = execute(server_commands, HOST, PORT)
print(f"{i} + 1j * {q}")
[[1]] + 1j * [[2]]
For multiple readout pulses, on the same dac:
from qibosoq.client import execute
from qibosoq.components.base import (
Qubit,
OperationCode,
Config,
Parameter
)
from qibosoq.components.pulses import Rectangular
pulse_1 = Rectangular(
frequency = 6400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0,
duration = 0.04,
name = "readout_pulse_0",
type = "readout",
dac = 1,
adc = 0
)
pulse_2 = Rectangular(
frequency = 6400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0.04,
duration = 2,
name = "readout_pulse",
type = "readout",
dac = 1,
adc = 0
)
sequence = [pulse_1, pulse_2]
config = Config()
qubit = Qubit()
server_commands = {
"operation_code": OperationCode.EXECUTE_PULSE_SEQUENCE,
"cfg": config,
"sequence": sequence,
"qubits": [qubit],
}
i, q = execute(server_commands, HOST, PORT)
print(f"{i} + 1j * {q}")
[[1, 5]] + 1j * [[2, 9]]
While if the measurement is done on a different adc the result will be slightly different:
from qibosoq.client import execute
from qibosoq.components.base import (
Qubit,
OperationCode,
Config,
Parameter
)
from qibosoq.components.pulses import Rectangular
pulse_1 = Rectangular(
frequency = 6400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0,
duration = 0.04,
name = "readout_pulse_0",
type = "readout",
dac = 2,
adc = 1
)
pulse_2 = Rectangular(
frequency = 6400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0.04,
duration = 2,
name = "readout_pulse",
type = "readout",
dac = 1,
adc = 0
)
sequence = [pulse_1, pulse_2]
config = Config()
qubit = Qubit()
server_commands = {
"operation_code": OperationCode.EXECUTE_PULSE_SEQUENCE,
"cfg": config,
"sequence": sequence,
"qubits": [qubit],
}
i, q = execute(server_commands, HOST, PORT)
print(f"{i} + 1j * {q}")
[[1], [5]] + 1j * [[2], [9]]
Execution of a sweeper experiment¶
A sweeper is a fast scan on a pulse parameter, executed on the FPGA logic to maximize the speed.
from qibosoq.client import execute
from qibosoq.components.base import (
Qubit,
OperationCode,
Config,
Sweeper,
Parameter
)
from qibosoq.components.pulses import Rectangular
pulse_1 = Rectangular(
frequency = 5400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0,
duration = 0.04,
name = "drive_pulse",
type = "drive",
dac = 0,
adc = None
)
pulse_2 = Rectangular(
frequency = 6400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0.04,
duration = 2,
name = "readout_pulse",
type = "readout",
dac = 1,
adc = 0
)
sequence = [pulse_1, pulse_2]
config = Config()
qubit = Qubit()
sweeper = Sweeper(
parameters = [Parameter.AMPLITUDE],
indexes = [0],
starts = [0],
stops = [1],
expts = 100
)
server_commands = {
"operation_code": OperationCode.EXECUTE_SWEEPS,
"cfg": config,
"sequence": sequence,
"qubits": [qubit],
"sweepers": [sweeper],
}
i, q = execute(server_commands, HOST, PORT)
print(f"{i} + 1j * {q}")
[[1, 2, 3]] + 1j * [[6, 7, 8]]
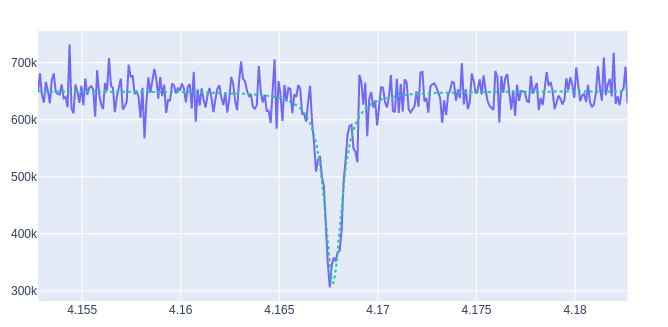
Example of a qubit spectroscopy¶
As a real example, let’s perform a qubit spectroscopy experiment.
We first import all the needed qibosoq components and matplotlib for plotting:
import numpy as np
from qibosoq.client import execute
from qibosoq.components.base import (
Qubit,
OperationCode,
Config,
Sweeper,
Parameter
)
from qibosoq.components.pulses import Rectangular
In a qubit spectroscopy experiment we send two pulses: the first drives a qubit but has a variable frequency (we will use a sweeper) and the second is a fix readout pulse.
pulse_1 = Rectangular(
frequency = 5400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0,
duration = 0.04,
name = "drive_pulse",
type = "drive",
dac = 0,
adc = None
)
pulse_2 = Rectangular(
frequency = 6400, #MHz
amplitude = 0.05,
relative_phase = 0,
start_delay = 0.04,
duration = 2,
name = "readout_pulse",
type = "readout",
dac = 1,
adc = 0
)
sequence = [pulse_1, pulse_2]
Next, we can define the sweeper:
from qibosoq.components.base import Sweeper, Parameter
sweeper = Sweeper(
parameters = [Parameter.FREQUENCY],
indexes = [0],
starts = [4154],
stops = [4185],
expts = 150
)
Now we can define the qibosoq.components.base.Config object and our qibosoq.components.base.Qubit object:
config = Config(
relaxation_time = 10,
reps = 2000
)
qubit = Qubit(
bias = 0.1,
dac = 3
)
And we can execute and plot the results:
server_commands = {
"operation_code": OperationCode.EXECUTE_SWEEPS,
"cfg": config,
"sequence": sequence,
"qubits": [qubit],
"sweepers": [sweeper],
}
i, q = execute(server_commands, HOST, PORT)
And we can plot the final rsults with:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
frequency = np.linspace(sweeper.starts[0], sweeper.stops[0], sweeper.expts)
results = np.array((i[0][0]) + 1j * np.array(q[0][0]))
plt.plot(frequency, np.abs(results))